It is impossible to predict the onset of schizophrenic psychosis. If factors linked to a risk of psychosis can be identified, however, these may yield significant insights into its underlying mechanisms. Basel-based scientists have now established a link between particular genes and the size of important brain structures in individuals with an elevated risk of psychosis. The results of the study appear in the latest edition of the scientific journal Translational Psychiatry.
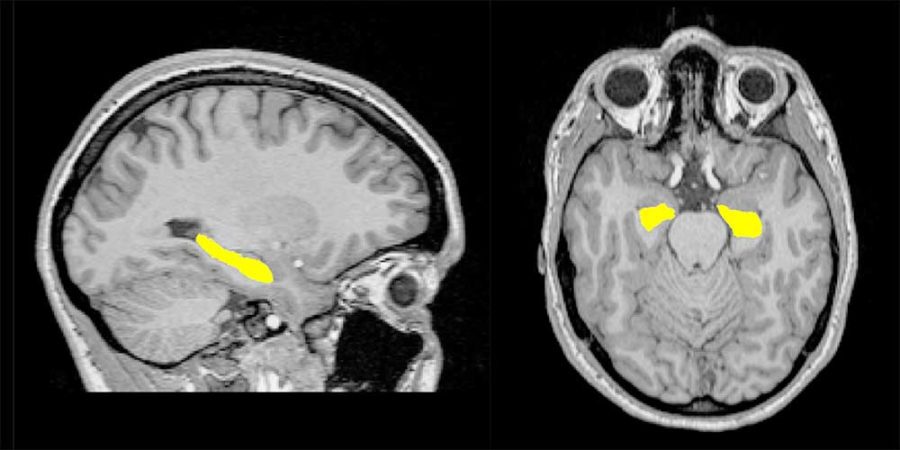
Schizophrenic psychoses are a frequently occurring group of psychiatric disorders caused by a combination of biological, social and environmental factors. These disorders are associated with changes to the brain structure: for example, the hippocampus in the temporal lobe is usually smaller in affected individuals than in healthy ones. It is not yet known whether these changes to the brain structure are a result of the disorders and their accompanying medications, or whether they are already present before the onset of symptoms.
Together with a research group from the University of Basel, Fabienne Harrisberger and Stefan Borgwardt examined the brain structures of individuals exhibiting an elevated risk of psychosis, and those of individuals experiencing the onset of psychotic symptoms for the first time. Initially, scientists from the Adult Psychiatric Clinic of the University Psychiatric Clinics (UPK) and the Transfaculty Research Platform Molecular and Cognitive Neurosciences (MCN) observed no appreciable difference between the hippocampi of individuals at high risk and those of patients.
Next, together with scientists from the Transfaculty Research Platform, they investigated whether any known schizophrenia risk genes are associated with the hippocampus. This appears to be the case: the greater the number of risk genes a person possessed, the smaller the volume of their hippocampus – regardless of whether they were a high-risk study participant or a patient. This means that a group of risk genes is connected with a reduction in the size of a critical region of the brain before the disorder manifests itself.

Potential for differentiated therapy
This result is significant for the understanding of neurobiological factors contributing to schizophrenia. It is well-known that none of the wider risk factors (e.g. genes, environment, unfavorable social situation) can be used to predict the onset of psychosis in a specific individual. However, the discovery may be of use for the treatment of schizophrenia.
“It is quite possible that individuals with smaller hippocampi will react differently to therapy compared to those with normally developed hippocampi,” explains Prof. Stefan Borgwardt of the Neuropsychiatry and Brain Imaging Unit. Further studies to ascertain the therapeutic potential of this research are planned.
Original article
Fabienne Harrisberger, Renata Smieskova, Christian Vogler, Tobias Egli, André Schmidt, Claudia Lenz, Andor E Simon, Anita Riecher-Rössler, Andreas Papassotiropoulos, Stefan Borgwardt
Impact of polygenic schizophrenia-related risk and hippocampal volumes on the onset of psychosis
Translational Psychiatry (2016), doi: 10.1038/TP.2016.143