Just a few doses of an experimental drug can reverse age-related declines in memory and mental flexibility in mice, according to a new study by UC San Francisco scientists. The drug, called ISRIB, has already been shown in laboratory studies to restore memory function months after traumatic brain injury (TBI), reverse cognitive impairments in Down Syndrome, prevent noise-related hearing loss, fight certain types of prostate cancer, and even enhance cognition in healthy animals.
In the new study, published Dec. 1, 2020, in the open-access journal eLife, researchers showed rapid restoration of youthful cognitive abilities in aged mice, accompanied by a rejuvenation of brain and immune cells that could help explain improvements in brain function.
“ISRIB’s extremely rapid effects show for the first time that a significant component of age-related cognitive losses may be caused by a kind of reversible physiological “blockage” rather than more permanent degradation,” said Susanna Rosi, PhD, Lewis and Ruth Cozen Chair II and professor in the departments of Neurological Surgery and of Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Science.
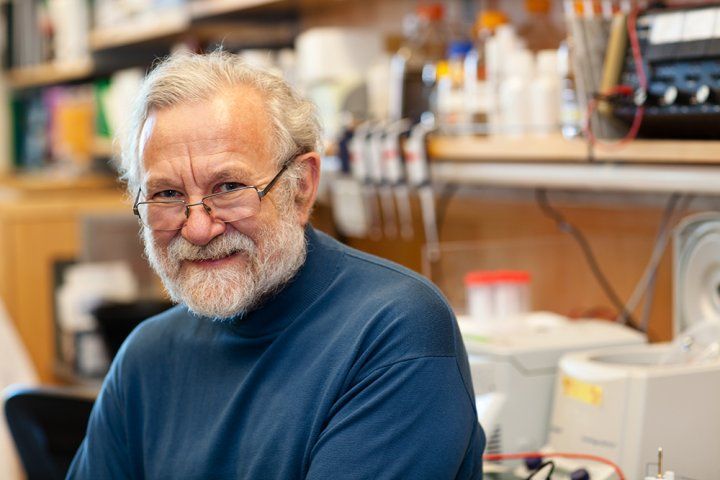
“The data suggest that the aged brain has not permanently lost essential cognitive capacities, as was commonly assumed, but rather that these cognitive resources are still there but have been somehow blocked, trapped by a vicious cycle of cellular stress,” added Peter Walter, PhD, a professor in the UCSF Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. “Our work with ISRIB demonstrates a way to break that cycle and restore cognitive abilities that had become walled off over time.”
Could Rebooting Cellular Protein Production Hold the Key to Aging and Other Diseases?
Walter has won numerous scientific awards, including the Breakthrough, Lasker and Shaw prizes, for his decades-long studies of cellular stress responses. ISRIB, discovered in 2013 in Walter’s lab, works by rebooting cells’ protein production machinery after it gets throttled by one of these stress responses – a cellular quality control mechanism called the integrated stress response (ISR; ISRIB stands for ISR InhiBitor).

The ISR normally detects problems with protein production in a cell — a potential sign of viral infection or cancer-promoting gene mutations — and responds by putting the brakes on cell’s protein-synthesis machinery. This safety mechanism is critical for weeding out misbehaving cells, but if stuck in the on position in a tissue like the brain, it can lead to serious problems, as cells lose the ability to perform their normal activities, Walter and colleagues have found.
In particular, recent animal studies by Walter and Rosi, made possible by early philanthropic support from The Rogers Family Foundation, have implicated chronic ISR activation in the persistent cognitive and behavioral deficits seen in patients after TBI, by showing that, in mice, brief ISRIB treatment can reboot the ISR and restore normal brain function almost overnight.
The cognitive deficits in TBI patients are often likened to premature aging, which led Rosi and Walter to wonder if the ISR could also underlie purely age-related cognitive decline. Aging is well known to compromise cellular protein production across the body, as life’s many insults pile up and stressors like chronic inflammation wear away at cells, potentially leading to widespread activation of the ISR.
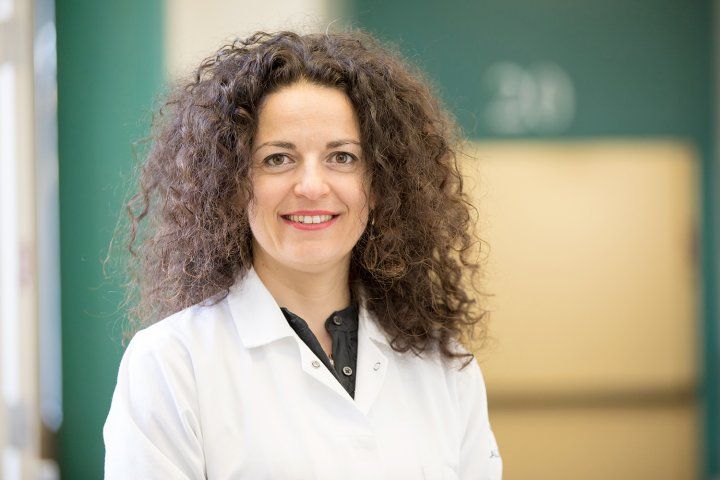
“We’ve seen how ISRIB restores cognition in animals with traumatic brain injury, which in many ways is like a sped-up version of age-related cognitive decline,” said Rosi, who is director of neurocognitive research in the UCSF Brain and Spinal Injury Center and a member of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. “It may seem like a crazy idea, but asking whether the drug could reverse symptoms of aging itself was just a logical next step.”
Improves Cognition, Boosts Neuron and Immune Cell Function
In the new study, researchers led by Rosi lab postdoc Karen Krukowski, PhD, trained aged animals to escape from a watery maze by finding a hidden platform, a task that is typically hard for older animals to learn. But animals who received small daily doses of ISRIB during the three-day training process were able to accomplish the task as well as youthful mice, much better than animals of the same age who didn’t receive the drug.
The researchers then tested how long this cognitive rejuvenation lasted and whether it could generalize to other cognitive skills. Several weeks after the initial ISRIB treatment, they trained the same mice to find their way out of a maze whose exit changed daily – a test of mental flexibility for aged mice who, like humans, tend to get increasingly stuck in their ways. The mice who had received brief ISRIB treatment three weeks before still performed at youthful levels, while untreated mice continued to struggle.
To understand how ISRIB might be improving brain function, the researchers studied the activity and anatomy of cells in the hippocampus, a brain region with a key role in learning and memory, just one day after giving animals a single dose of ISRIB. They found that common signatures of neuronal aging disappeared literally overnight: neurons’ electrical activity became more sprightly and responsive to stimulation, and cells showed more robust connectivity with cells around them while also showing an ability to form stable connections with one another usually only seen in younger mice.

The researchers are continuing to study exactly how the ISR disrupts cognition in aging and other conditions and to understand how long ISRIB’s cognitive benefits may last. Among other puzzles raised by the new findings is the discovery that ISRIB also alters the function of the immune system’s T cells, which also are prone to age-related dysfunction. The findings suggest another path by which the drug could be improving cognition in aged animals, and could have implications for diseases from Alzheimer’s to diabetes that have been linked to heightened inflammation caused by an aging immune system.
“This was very exciting to me because we know that aging has a profound and persistent effect on T cells and that these changes can affect brain function in the hippocampus,” said Rosi. “At the moment, this is just an interesting observation, but it gives us a very exciting set of biological puzzles to solve.”
Broad Effects Exemplify ‘Serendipity’ of Basic Research
Rosi and Walter were introduced by neuroscientist Regis Kelly, PhD, executive director of the University of California’s QB3 biotech innovation hub, following Walter’s 2013 study showing that the drug seemed to instantly enhance cognitive abilities in healthy mice. To Rosi, the results from that study implied some walled-off cognitive potential in the brain that the molecule was somehow unlocking, and she wondered if this extra cognitive boost might benefit patients with neurological damage from traumatic brain injury.