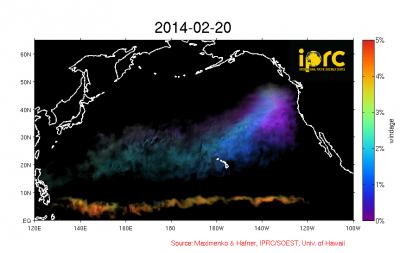
The amount of debris in the ocean is growing exponentially, becoming more and more hazardous and harmful to marine life and therefore also to our ocean food source. Measuring and tracking the movements of such debris are still in their infancy. The driftage generated by the tragic 2011 tsunami in Japan gave scientists Nikolai Maximenko and Jan Hafner a unique chance to learn about the effects of the ocean and wind on floating materials as they move across the North Pacific Ocean.
Shortly after the tsunami struck, Maximenko and Hafner used the IPRC Ocean Drift Model to predict where the debris from the tsunami would go. Their computer model is based on trajectories of real satellite-tracked drifting buoys and satellite-measured winds.
The model has now been charting the possible paths of the tsunami driftage for nearly 3 years. The scientists have made a major improvement to the initial model: it now accommodates objects of different shapes and buoyancies that expose different amounts of surface to the wind and travel at different speeds and different trajectories. The model therefore now includes different levels of wind-forcing, simulating the movement of different types of floating debris.
No formal marine debris observing systems exist to verify the model simulations. The model paths for tsunami debris, however, agree with reports of such debris washing up on the shores of Oregon, Washington, Alaska, and the Hawaiian Islands, as well as with observations by sailors crossing the North Pacific.