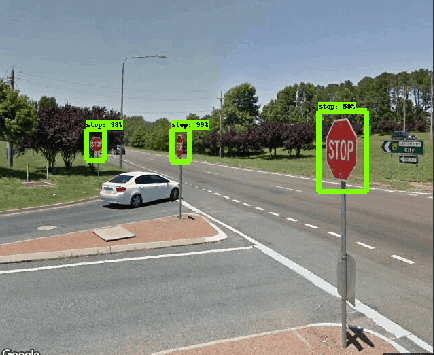
Geospatial scientists have developed a new program to monitor street signs needing replacement or repair by tapping into Google Street View images.
The fully-automated system is trained using AI-powered object detection to identify street signs in the freely available images
Authorities currently spend large amounts of time and money monitoring and recording the geo-location of traffic infrastructure manually, a task which also exposes workers to unnecessary traffic risks.
Results just published in the journal of Computers, Environment and Urban Systems show the system detects signs with near 96% accuracy, identifies their type with near 98% accuracy and can record their precise geo location from the 2D images.
Study lead author and RMIT University Geospatial Science Honours student, Andrew Campbell, said the proof-of-concept model was trained to see ‘stop’ and ‘give way’ signs, but could be trained to identify many other inputs and was easily scalable for use by local governments and traffic authorities.
“Councils have requirements to monitor this infrastructure but currently no cheap or efficient way to do so,” Campbell said.
“By using free and open source tools, we’ve now developed a fully automated system for doing that job, and doing it more accurately.”
The team found during investigations that mandatory GPS location data in existing street sign databases was often inaccurate, sometimes up to 10m off
“Tracking these signs manually by people who may not be trained geoscientists introduces human error into the database. Our system, once set up, can be used by any spatial analyst – you just tell the system which area you want to monitor and it looks after it for you,” Campbell said.
Campbell credited the project’s initial concept to his industry mentor at Alpine Shire Council and RMIT Geospatial Science alumnus, Barrett Higman, as well as industry partner Spatial Vision.
RMIT geospatial scientist and project co-lead, Dr Chayn Sun, said the fact that some councils were already attaching cameras onto rubbish trucks to gather street footage showed how valuable visual data were becoming, given what technology could now do with it.
“This imagery is critical for local governments in monitoring and managing assets and with the huge amount of geospatial applications flourishing, this information will only become more valuable,” Sun said.
“Ours is one of several early applications for this to meet a specific industry need but a whole lot more will emerge in coming years.”
Sun said footage from other sources, like that from rubbish truck cameras or any other geo-referenced imagery of the road network collected by councils, could also be fed into the system.
“Where footage is already being gathered, our research can provide councils with an economical tool to drive insights and data from this existing resource,” she said.
The project was co-led by Sun and fellow RMIT geospatial scientist Dr Alan Both, from the university’s Centre for Urban Research.
The team is currently working with local governments on heat intervention strategies using Google Street View images to analyse street tree shade.
‘Detecting and mapping traffic signs from Google Street View using deep learning and GIS’ was just published in Computers, Environment and Urban Systems with DOI: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2019.101350.
RMIT University was recently voted best geospatial science research institute in the world by the Geospatial World Forum.