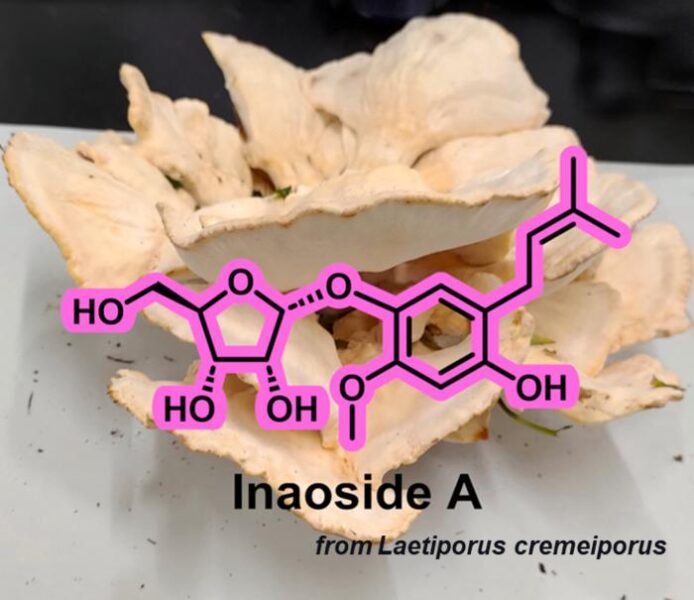
Researchers from Shinshu University have identified a new antioxidant compound called Inaoside A from the Laetiporus cremeiporus mushroom. This finding highlights the potential of mushrooms as a source of therapeutic bioactive compounds and could lead to the development of new antioxidant-based therapies for various health conditions.
The study, led by Assistant Professor Atsushi Kawamura is the first to isolate an antioxidant compound from L. cremeiporus.
“Our study marks the pioneering discovery of Inaoside A from an extract of the edible mushroom Laetiporus cremeiporus. To date, there has been only one prior report on the biological function of an extract of L. cremeiporus. We are the first to uncover the isolation of an antioxidant compound from L. cremeiporus,” said Kawamura.
The researchers collected fresh fruiting bodies of L. cremeiporus from the Ina campus of Shinshu University and used advanced chromatographic techniques to isolate Inaoside A, along with three other well-known bioactive compounds. They determined the structure of Inaoside A using NMR and other spectroscopic analyses, revealing its unique molecular formula and distinctive ribose moiety.
Tests showed that Inaoside A exhibited significant antioxidant properties, with an 80% inhibition of DPPH radicals at 100 μg/mL and an IC50 value of 79.9 μM. These findings suggest that Inaoside A could be a promising candidate for the development of new antioxidant-based therapies.
“We are now focusing on investigating the chemical compositions and biological properties of natural compounds obtained from mushrooms. Our goal is to uncover the potential of edible mushrooms as functional foods through this discovery,” Kawamura adds.
The discovery of Inaoside A marks a significant breakthrough in natural product research, and further studies will focus on synthetic research and detailed investigations into its biological activity to harness its potential as a pharmaceutical lead compound.
#MushroomAntioxidant #InaosideA #NaturalProductResearch #BioactiveMolecules