As lunar exploration missions shift from exploration to construction and utilization, in situ lunar construction becomes a critical requirement. The core of this process lies in regolith solidification and formation, which aims to maximize local resource utilization while minimizing transportation and maintenance costs. Professor Feng from Tsinghua University has conducted a comprehensive review, precise classification, and quantitative evaluation of regolith solidification and formation techniques, highlighting key challenges and future development directions.
Four Categories of Regolith Solidification and Formation Technologies
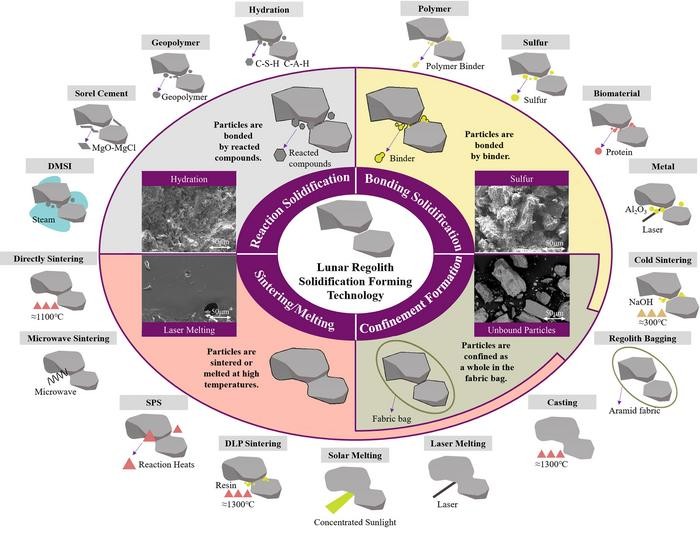
Based on the technical mechanisms of bonding and cohesion between particles, regolith solidification and formation technologies can be categorized into four groups: reaction solidification (RS), sintering/melting (SM), bonding solidification (BS), and confinement formation (CF) methods. Each category has specific implementation requirements and capabilities, with variations in the percentage of local regolith used, temperature requirements, and solidification time.
Evaluating Techniques for Cost-Effective and High-Performance Lunar Construction Materials
Researchers face the challenge of minimizing resource consumption, energy requirements, and operational complexity while ensuring reliability in the lunar environment. The research team introduces the 8IMEM quantification method, which includes eight evaluation indicators and scoring thresholds tailored to construction needs. According to the evaluation results, regolith bagging emerges as the highest-rated technique, offering promising prospects for large-scale in situ lunar construction. Sintering/melting techniques and casting techniques also rank high, with the latter being suitable for manufacturing critical components.
A Four-Stage Plan for Lunar Infrastructure Development
To align with lunar construction conditions and the long-term goals of the International Lunar Research Stations, a comprehensive four-stage plan has been devised: Laboratory, Research Station, Residence, and Habitat. Each stage has specific functions and distinct construction objectives, ensuring a progressive and sustainable development of lunar infrastructure. The research team analyzed the structural construction objectives for each stage and proposed regolith bag technology as a solution for lunar base construction based on quantitative evaluations.
Paving the Way for Optimized Lunar Construction Endeavors
By leveraging the insights derived from this comprehensive evaluation, researchers can make informed decisions on material preparation techniques, paving the way for optimized lunar construction endeavors. The proposed lunar habitat design based on regolith bags serves as a practical reference for future research. As lunar exploration continues to advance, the development of efficient and reliable in situ construction methods will be crucial for establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon.
Open Access Research and Additional Resources
The paper “Lunar In Situ Large-Scale Construction: Quantitative Evaluation of Regolith Solidification Techniques,” authored by Charun Bao, Daobo Zhang, Qinyu Wang, Yifei Cui, Peng Feng, is available as an open access publication at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.03.004. For more information about the Engineering journal, follow them on Twitter (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) and like them on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).