Transgender individuals often face unique challenges in aligning their physical bodies with their true gender identity. Among the various methods employed, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) stands as a vital means for transgender men to achieve physical changes in consonance with their gender identity. Navigating the complexities that come with gender transition, transgender individuals seek medical interventions to alleviate gender dysphoria and align their bodies with their gender identity.
For transgender men, testosterone therapy holds promise in inducing masculinizing effects such as increased muscle mass, cessation of menstruation, and deepening of the voice. However, the lack of comprehensive research on the long-term effects and safety of testosterone therapy poses significant challenges in clinical decision-making and underscores the persistent taboo surrounding transgender healthcare. To address this pressing need, a study led by Assistant Professor Yusuke Tominaga along with Dr. Tomoko Kobayashi and Dr. Motoo Araki from the Department of Urology, Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama, Japan dives into understanding the long-term physical effects and safety profile of testosterone therapy for transgender men, shedding light on crucial aspects of hormone administration and its impact on body composition. Their research findings were published in Andrology on 2 April 2024.
“The research team was inspired to investigate this area as we noticed the lack of a standardized regimen for testosterone dosage and administration. Our aim was to understand how hormone dosages are adjusted to align more closely with typical male testosterone levels in the bloodstream,” explains Dr. Tominaga.
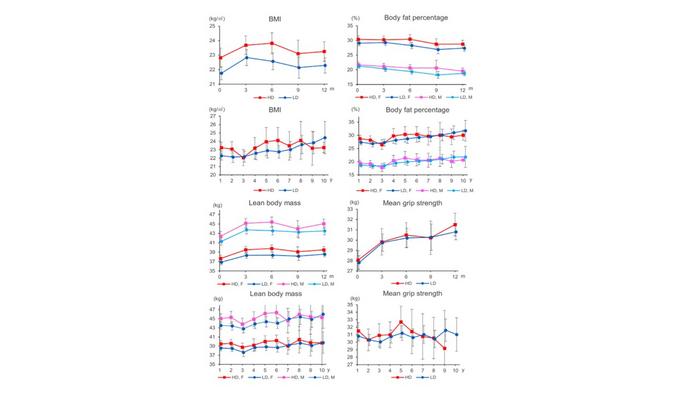
Analyzing data from transgender men who commenced GAHT between May 2000 and December 2021, the researchers meticulously recorded physical findings, blood test results, and menstrual cessation rates. They then compared the effects of testosterone on body composition changes and laboratory parameters, stratifying participants into low-dose and high-dose groups based on their testosterone dosage.
The findings of the study revealed that both low-dose and high-dose testosterone regimens demonstrated favorable outcomes, with no significant differences observed in menstrual cessation rates up to 12 months. Over time, participants exhibited a decrease in body fat percentage and an increase in lean body mass, indicative of the desired masculinizing effects of testosterone therapy.
Notably, the high-dose group exhibited greater gains in lean body mass during the initial year of therapy, suggesting a potential strategy for individuals seeking more rapid changes in body composition. Importantly, the study found no evidence of long-term, dose-dependent side effects such as polycythemia or dyslipidemia, reassuring both clinicians and transgender individuals regarding the safety profile of testosterone therapy.
Reflecting on the significance of their findings, Dr. Tominaga explains, “Our study contributes valuable evidence on the long-term effects of testosterone therapy, providing crucial insights for clinicians managing transgender healthcare. By elucidating the safety and efficacy of hormone therapy, we hope to alleviate uncertainties surrounding transgender healthcare and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their treatment.”
This study opens the door to more inclusive and evidence-based care by illuminating the long-term effects and safety of testosterone therapy for transgender men.