Summary: Researchers at Nagoya University have discovered that a soy protein called β-conglycinin can help prevent heart failure progression in mice by positively affecting gut bacteria. The protein increases production of beneficial short-chain fatty acids, suggesting potential new dietary approaches to heart health.
Journal: Clinical Nutrition, September 2024, DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.09.045
Reading time: 3 minutes
The link between heart health and diet has taken an unexpected turn through the gut. New research published in Clinical Nutrition reveals how a specific protein found in soybeans might help protect against heart failure by influencing intestinal bacteria.
From Soybeans to Heart Protection
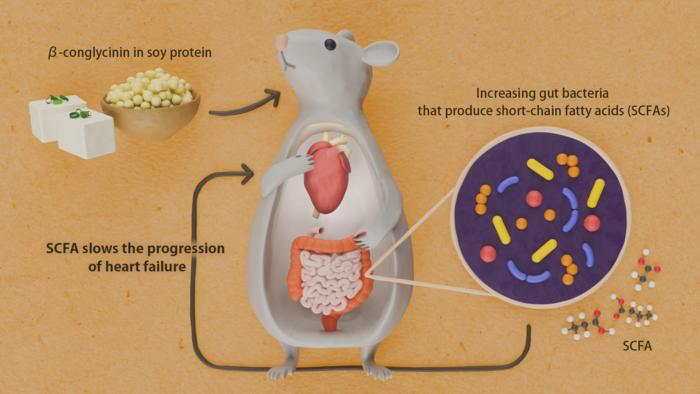
A team from Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine investigated β-conglycinin (β-CG), a protein found in soybeans. When fed to mice prone to heart failure, the protein improved heart function and reduced common signs of heart disease such as muscle thickening and tissue scarring.
“An important aspect of this study is that functional soy components showed beneficial effects on the heart,” says Dr. Nozomi Furukawa. “Previously, effects on obesity have been shown, but the effects on cardiovascular disease were not known.”
The Gut-Heart Connection
The study revealed that β-CG increases three types of beneficial bacteria in the gut: Butyricimonas, Marvinbryantia, and Anaerotruncus. These bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that help maintain gut health and may protect the heart from damage caused by high blood pressure.
To verify this connection, researchers used antibiotics to reduce these bacteria in mice, which eliminated β-CG’s protective effects. When they administered sodium propionate, one of the SCFAs, directly to mice, it produced similar heart-protective results as β-CG.
Future Applications and Limitations
While the findings are promising, researchers note some limitations. “Of course, soy and its components, such as β-CG, may not be effective for all people, especially those with allergies,” Furukawa explains. The team plans to investigate the detailed molecular mechanisms to develop new treatments.
Glossary of Terms
- β-conglycinin (β-CG): A protein found in soybeans that may help protect heart health
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs): Beneficial compounds produced by gut bacteria during digestion
- Gut microbiota: The community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract
- Heart failure: A condition where the heart cannot pump blood effectively
Test Your Knowledge
What three types of bacteria were increased by β-CG?
Butyricimonas, Marvinbryantia, and Anaerotruncus
How did researchers confirm the role of gut bacteria in heart protection?
They used antibiotics to reduce the bacteria population, which eliminated β-CG’s protective effects
What specific improvements did mice show when fed β-CG?
Improved heart function, less muscle thickening, and reduced scarring of heart tissue
What is a key limitation of this potential treatment?
It may not be effective for all people, especially those with soy allergies
Enjoy this story? Get our newsletter! https://scienceblog.substack.com/