annals of internal medicine
Obesity and knee osteoarthritis shorten healthy years of life
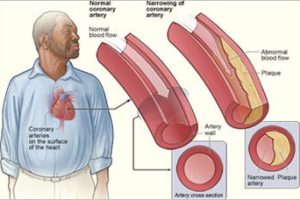
Boston, MA — An estimated 10 million Americans suffer from knee osteoarthritis (OA), making it one of the most common causes of disability in the US. Due to obesity and symptomatic knee OA, Americans over the age of 50 will together lose the equiv…
Storytelling may help control blood pressure in African-Americans
Controlling blood pressure is not only a medical challenge, but a social one as well. Because patients are required to strictly adhere to a treatment plan that may include medication, dietary restrictions and regular doctor visits, the ideas of we…
Not following doctor’s orders: Prescription abandonment
INDIANAPOLIS — Failure to have a prescription filled can undermine medical treatment, result in increased health care costs and potentially have devastating results for the patient. An editorial in the Nov. 16 issue of the Annals of Internal Medic…
Diabetic adults’ conditions improved after phone calls with fellow patients
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Phone calls with a peer facing the same self-management challenges helped diabetes patients manage their conditions and improved their blood sugar levels better than those who used traditional nurse care management services alo…
Restriction or ban of ephedra supported by first comparative herbal study
The first comparative study to examine the risk of taking ephedra with that of taking other commonly used herbs calls into question the herbal stimulant’s current standing as an unrestricted dietary supplement. Researchers found that products containing ephedra accounted for less than 1 percent of the herbal supplement sales in the United States in 2001. These products, however, were responsible for 62 percent of all herbal-related reports made to poison control centers nationwide that year, according to the study by researchers at the San Francisco VA Medical Center (SFVAMC).
Minimum smallpox vaccination is best strategy for now, experts say
The current smallpox vaccination policy of vaccinating a very limited number of first responders to a potential smallpox outbreak and avoiding mass vaccination is the best vaccination strategy, say two smallpox experts in an article in Annals of Internal Medicine. The article is released today online at www.annals.org and will be published in the March 18, 2003, hard copy edition of the journal. In the absence of a known threat of smallpox exposure, mass vaccination of the entire population or selective or voluntary vaccination would be dangerous to many who might get the vaccine, their contacts and the public health initiative, say J. Michael Lane, MD, MPH and Joel Goldstein, MD, in the article.
Suppressing Immune System Reverses Untreatable Case of Blood Disease
Treatment with two medications that suppress the immune system, rituximab and cyclophosphamide, appears to have cured one woman of an otherwise untreatable case of the blood disease known as thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). The findings support the theory that TTP is an autoimmune disease, and not only provide insight into diagnosis and treatment, but also reveal clues about blood clotting and autoimmune diseases in general.
Evidence Lacking on Use of Routine Prostate Cancer Screening
Although screening for prostate cancer is a common part of a routine checkup for American men, a new finding issued today from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concludes there is insufficient scientific evidence to promote routine screening for all men and inconclusive evidence that early detection improves health outcomes. The finding is published in the December 3 issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine.