argonne national laboratory
Small reactors could figure into US energy future
A newly released study from the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC) concludes that small modular reactors may hold the key to the future of U.S. nuclear power generation.
“Clearly, a robust commercial SMR industry is highly adv…
Chemists document workings of key staph enzyme — and how to block it
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers have determined the structure and mechanism of an enzyme that performs the crucial first step in the formation of cholesterol and a key virulence factor in staph bacteria.
Chemists at the University of Illino…
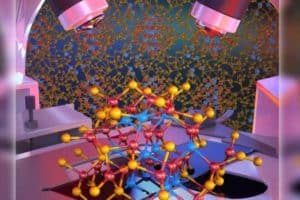
Tiny 3-D images shed light on origin of Earth’s core
To answer the big questions, it often helps to look at the smallest details. That is the approach Stanford mineral physicist Wendy Mao is taking to understanding a major event in Earth’s inner history. Using a new technique to scrutinize how minute …
APS releases report on renewable energy and the electricity grid
WASHINGTON, D.C. — U.S. policymakers must focus more closely on developing new energy storage technologies as they consider a national renewable electricity standard, according to one of the principal recommendations in a newly released report, Int…
Molecular fossil
In today’s world of sophisticated organisms proteins are the stars. They are the indispensible catalytic workhorses, carrying out the processes essential to life. But long, long ago ribonucleic acid (RNA) reigned supreme.
Now Northwestern Universi…
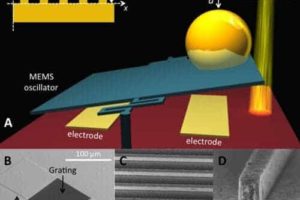
Vacuum arcs spark new interest
Whenever two pieces of metal at different voltages are brought near each other, as when an appliance is plugged into a live socket, there is a chance there will be an arc between them. Most of the arcs people see are a breakdown of the gas bet…
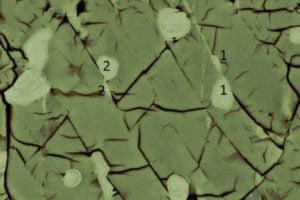
Researchers uncover novel self-assembly of Alzheimer’s amyloid fibrils
Researchers at Emory University and Argonne National Laboratory have discovered a new method to manipulate the self-assembly and formation of amyloid fibrils, a major component of brain plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease, thereby opening new avenues for examination of their formation and for the construction of robust nanotubes that have potential applications in research, industry and medicine.