A study published in Science Translational Medicine performed at the Latner Thoracic Surgery Research Laboratories and UHN’s Ajmera Transplant Centre has proved that it is possible to convert blood type safely in donor organs intended for transplantation. This finding is an important step towards creating universal type O organs, which would significantly improve fairness in organ allocation and decrease mortality for patients in the waitlist.
“With the current matching system, wait times can be considerably longer for patients who need a transplant depending on their blood type,” explains Dr. Marcelo Cypel, Surgical Director of the Ajmera Transplant Centre and the senior author of the study.
“Having universal organs means we could eliminate the blood-matching barrier and prioritize patients by medical urgency, saving more lives and wasting less organs,” adds Dr. Cypel, who is also a Thoracic Surgeon at UHN’s Sprott Department of Surgery, a Professor in the Department of Surgery at U of T and the Canada Research Chair in Lung Transplantation.
Blood type is determined by the presence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells — type A blood has the A antigen, B has the B antigen, AB blood has both antigens and O has none. Antigens can trigger an immune response if they are foreign to our bodies. That is why for blood transfusions we can only receive blood from donors with the same blood type as ours, or universal type O.
Likewise, antigens A and B are present on the surfaces of blood vessels in the body, including vessels in solid organs. If someone who is type O (meaning they have anti-A and anti-B antibodies in their blood stream) received an organ from a type A donor, for example, the organ in all likelihood would be rejected. Consequently, donor organs are matched to potential recipients in the waitlist based on blood type, among other criteria.
Patients who are type O wait on average twice as long to receive a lung transplant compared to patients who are type A, explains Dr. Aizhou Wang, Scientific Associate at Dr. Cypel’s lab and first author of the study.
“This translates into mortality. Patients who are type O and need a lung transplant have a 20% higher risk of dying while waiting for a matched organ to become available,” says Dr. Wang.
This disparity is also present for other organs, she adds, where a patient who is type O or B in need of a kidney transplant will be on the waitlist for an average of 4 to 5 years, compared to 2 to3 years for types A or AB.
“If you convert all organs to universal type O, you can eliminate that barrier completely.”
The experiment
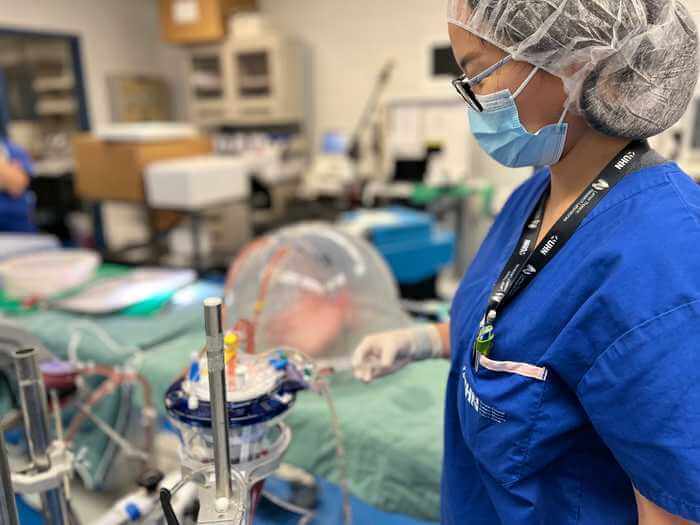
This proof-of-concept study was done at Dr. Cypel’s research lab, part of Latner Thoracic Surgery Research Laboratories. The experiment used the Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion (EVLP) System pioneered in Toronto as a platform for the treatment. The EVLP system pumps nourishing fluids through organs, enabling them to be warmed to body temperature, so that they can be repaired and improved before transplantation.
Human donor lungs not suitable for transplantation from type A donors were put in the EVLP circuit. One lung was treated with a group of enzymes to clear the antigens from the surface of the organ, while the other lung, from the same donor, remained untreated.
The team then tested each of the lungs by adding type O blood (with high concentrations of anti-A antibodies) to the circuit, to simulate an ABO incompatible transplant. The results demonstrated that the treated lungs were well tolerated while the untreated ones showed signs of rejection.
Gut enzymes key to creating universal organs
This study was successful because of important interdisciplinary efforts across multiple organizations in Canada, including UHN, University of Toronto, University of British Columbia and University of Alberta.
“By exchanging ideas across disciplines and across the country, we became one collaborative effort to tackle an important problem in organ transplantation,” says Dr. Wang.
UBC biochemist Dr. Stephen Withers and his team found a group of enzymes in 2018, which was key to this first step in creating universal blood-type organs. These enzymes were delivered to the lungs in this study using the EVLP circuit.
“Enzymes are Mother Nature’s catalysts and they carry out particular reactions. This group of enzymes that we found in the human gut can cut sugars from the A and B antigens on red blood cells, converting them into universal type O cells.
“In this experiment, this opened a gateway to create universal blood-type organs,” explains Dr. Withers.
“This is a great partnership with UHN and I was amazed to learn about the ex vivo perfusion system and its impact for transplants. It is exciting to see our findings being translated to clinical research,” adds Dr. Withers.
As next step, the team of researchers is working on a proposal for a clinical trial within the next 12 to 18 months.