national institute of allergy and infectious diseases
6-month drug regimen cuts HIV risk for breastfeeding infants, NIH study finds
Giving breastfeeding infants of HIV-infected mothers a daily dose of the antiretroviral drug nevirapine for six months halved the risk of HIV transmission to the infants at age 6 months compared with giving infants the drug daily for six weeks, acco…
CROI — Day 3: Selected highlights of NIH-supported research
The 18th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections is being held at the Hynes Convention Center in Boston from February 27 through March 2. Day three of this major HIV/AIDS research conference included the following selected present…
Border patrol: Immune cells protect body from invaders, according to Penn study
PHILADELPHIA – So-called barrier sites — the skin, gut, lung — limit the inner body’s exposure to allergens, pollutants, viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Understanding how the immune system works in these external surfaces has implications…
NIH, Gates Foundation and Colorado State team up to find new approach to a TB vaccine
WHAT:
A team of U.S. and European researchers have found that a new vaccine strategy tested in mice provides stronger, more long-lasting protection from tuberculosis (TB) infection than the vaccine currently used in humans, known as BCG. Their fin…
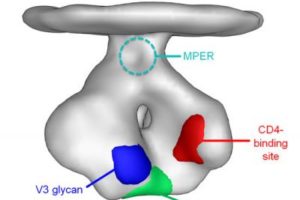
Sex, race, and geography influence health outcomes following primary HIV infection
Women, nonwhites, and people in the southern United States who were newly infected with HIV and followed for an average of four years experienced greater HIV/AIDS-related morbidity compared to men and people of other races living in other regions of…
Research identifies drug target for prion diseases, ‘mad cow’
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Jan. 4, 2011) − Scientists at the University of Kentucky have discovered that plasminogen, a protein used by the body to break up blood clots, speeds up the progress of prion diseases such as mad cow disease.
This finding m…
Milestone in fight against deadly disease
SEATTLE & CHICAGO — Scientists at Seattle Biomedical Research Institute (Seattle BioMed) and Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine have reached a major milestone in the effort to wipe out some of the most lethal diseases on the plane…
NIH scientists identify mechanism responsible for spreading biofilm infections
What: Scientists from the National Institutes of Health have discovered how catheter-related bacterial infection develops and disseminates to become a potentially life-threatening condition. The study, which included research on Staphylococcus epide…
NIH study suggests that early detection is possible for prion diseases
A fast test to diagnose fatal brain conditions such as mad cow disease in cattle and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans could be on the horizon, according to a new study from National Institutes of Health scientists. Researchers at NIH’s National I…