virginia commonwealth university
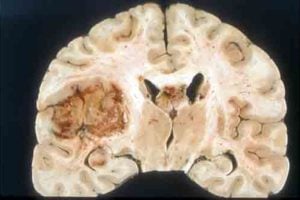
Brain tsunamis’ are clue to helping victims of major head injuries
Treating ‘brain tsunamis’ or ‘killer waves’ could stop many victims of major head injury from suffering additional brain damage, a study published in Lancet Neurology has found. Scientists have been investigating this phenomenon for decades, with the…
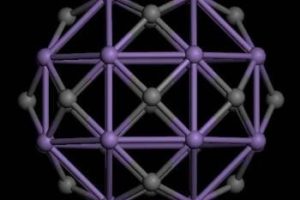
Researchers discover a new class of magic atomic clusters called superhalogens
RICHMOND, Va. (Feb. 11, 2011) — An international team of researchers has discovered a new class of magnetic superhalogens — a class of atomic clusters able to exhibit unusual stability at a specific size and composition, which may be used to adv…
VCU Massey first to combine targeted agents to kill multiple myeloma cells
Richmond, Va. (Feb. 10, 2011) — Scientists at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center have developed a novel treatment strategy for multiple myeloma that pairs two targeted agents to kill cancer cells. The study’s findings, published…
Could oysters be used to clean up Chesapeake Bay?
Madison, WI JANUARY 20, 2011 — Chronic water quality problems caused by agricultural and urban runoff, municipal wastewater, and atmospheric deposition from the burning of fossil fuels leads to oxygen depletion, loss of biodiversity, and harmful al…
VCU findings may help explain some major clinical symptoms of preeclampsia
RICHMOND, Va. (Jan. 4, 2011) — Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine researchers have found that a significant increase of an enzyme in the blood vessels of pregnant women with preeclampsia may explain some of the symptoms associat…
Women war veterans face higher risk of mental health problems during pregnancy
New Rochelle, NY, December 21, 2010 — Pregnancy among women veterans who served in Iraq and Afghanistan appears to increase their risk for mental health problems such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), according t…
Nanoscale gene ‘ignition switch’ may help spot and treat cancer
In a proof of principal study in mice, scientists at Johns Hopkins and the Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) have shown that a set of genetic instructions encased in a nanoparticle can be used as an “ignition switch” to rev up gene activity tha…