It’s a well-known fact that water, at sea level, starts to boil at a temperature of 212 degrees Fahrenheit, or 100 degrees Celsius. And scientists have long observed that when water is confined in very small spaces, its boiling and freezing points can change a bit, usually dropping by around 10 C or so.
But now, a team at MIT has found a completely unexpected set of changes: Inside the tiniest of spaces — in carbon nanotubes whose inner dimensions are not much bigger than a few water molecules — water can freeze solid even at high temperatures that would normally set it boiling.
The discovery illustrates how even very familiar materials can drastically change their behavior when trapped inside structures measured in nanometers, or billionths of a meter. And the finding might lead to new applications — such as, essentially, ice-filled wires — that take advantage of the unique electrical and thermal properties of ice while remaining stable at room temperature.
The results are being reported today in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, in a paper by Michael Strano, the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor in Chemical Engineering at MIT; postdoc Kumar Agrawal; and three others.
“If you confine a fluid to a nanocavity, you can actually distort its phase behavior,” Strano says, referring to how and when the substance changes between solid, liquid, and gas phases. Such effects were expected, but the enormous magnitude of the change, and its direction (raising rather than lowering the freezing point), were a complete surprise: In one of the team’s tests, the water solidified at a temperature of 105 C or more. (The exact temperature is hard to determine, but 105 C was considered the minimum value in this test; the actual temperature could have been as high as 151 C.)
“The effect is much greater than anyone had anticipated,” Strano says.
It turns out that the way water’s behavior changes inside the tiny carbon nanotubes — structures the shape of a soda straw, made entirely of carbon atoms but only a few nanometers in diameter — depends crucially on the exact diameter of the tubes. “These are really the smallest pipes you could think of,” Strano says. In the experiments, the nanotubes were left open at both ends, with reservoirs of water at each opening.
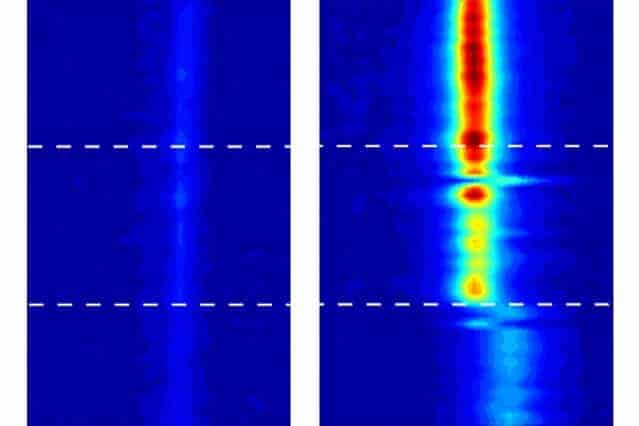
Even the difference between nanotubes 1.05 nanometers and 1.06 nanometers across made a difference of tens of degrees in the apparent freezing point, the researchers found. Such extreme differences were completely unexpected. “All bets are off when you get really small,” Strano says. “It’s really an unexplored space.”
In earlier efforts to understand how water and other fluids would behave when confined to such small spaces, “there were some simulations that showed really contradictory results,” he says. Part of the reason for that is many teams weren’t able to measure the exact sizes of their carbon nanotubes so precisely, not realizing that such small differences could produce such different outcomes.
In fact, it’s surprising that water even enters into these tiny tubes in the first place, Strano says: Carbon nanotubes are thought to be hydrophobic, or water-repelling, so water molecules should have a hard time getting inside. The fact that they do gain entry remains a bit of a mystery, he says.
Strano and his team used highly sensitive imaging systems, using a technique called vibrational spectroscopy, that could track the movement of water inside the nanotubes, thus making its behavior subject to detailed measurement for the first time.
The team can detect not only the presence of water in the tube, but also its phase, he says: “We can tell if it’s vapor or liquid, and we can tell if it’s in a stiff phase.” While the water definitely goes into a solid phase, the team avoids calling it “ice” because that term implies a certain kind of crystalline structure, which they haven’t yet been able to show conclusively exists in these confined spaces. “It’s not necessarily ice, but it’s an ice-like phase,” Strano says.
Because this solid water doesn’t melt until well above the normal boiling point of water, it should remain perfectly stable indefinitely under room-temperature conditions. That makes it potentially a useful material for a variety of possible applications, he says. For example, it should be possible to make “ice wires” that would be among the best carriers known for protons, because water conducts protons at least 10 times more readily than typical conductive materials. “This gives us very stable water wires, at room temperature,” he says.
The research team also included MIT graduate students Steven Shimizu and Lee Drahushuk, and undergraduate Daniel Kilcoyne. The work was supported by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory and the U.S. Army Research Office through the MIT Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies, and Shell-MIT Energy Initiative Energy Research Fund.
If our reporting has informed or inspired you, please consider making a donation. Every contribution, no matter the size, empowers us to continue delivering accurate, engaging, and trustworthy science and medical news. Independent journalism requires time, effort, and resources—your support ensures we can keep uncovering the stories that matter most to you.
Join us in making knowledge accessible and impactful. Thank you for standing with us!