A breakthrough imaging technique developed at Radboud university medical center has transformed the detection of rare pancreatic tumors, offering new hope for patients who often face years of uncertainty before diagnosis.
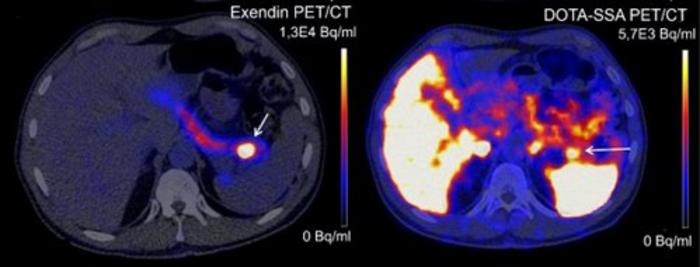
Summary: Scientists have developed a new PET scan based on a modified version of a Gila monster’s saliva compound that accurately identifies insulinomas – rare, benign pancreatic tumors – with unprecedented 95% success rate, compared to 65% with current methods.
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Understanding Insulinomas and Their Impact
The pancreas houses specialized cells called beta cells that produce insulin, a crucial hormone for blood sugar regulation. In rare cases, these cells develop into benign tumors called insulinomas, which overproduce insulin and cause dangerous drops in blood sugar.
“People with this condition have little energy due to low blood sugar and often faint,” explains Marti Boss, the study’s first author. “It’s a very challenging disease. It often takes a long time before patients get a diagnosis.”
Revolutionary Detection Method
The new Exendin-PET scan represents a significant advance over traditional imaging techniques. In a study involving 69 adult patients, it detected tumors in 95% of cases, marking a substantial improvement over current methods.
“In the past, surgeons would start cutting away portions of the pancreas until they found the tumor,” says Martin Gotthardt, professor of Nuclear Medicine at Radboudumc. “If it was at the end, the entire pancreas would be gone. You can live without a pancreas, but you’d struggle with severe diabetes and would constantly have to manage your blood sugar. So, a better scan was urgently needed.”
The Science Behind the Solution
The innovative scan utilizes a modified version of a compound found in Gila monster saliva. “We knew this substance specifically binds to a molecule on these tumors, the GLP1 receptor,” Gotthardt explains. “The substance from the saliva wasn’t very stable in the human body, so we created a more chemically stable version, called Exendin.”
Glossary of Terms
- Insulinoma: Benign tumor of the pancreatic beta cells
- Beta Cells: Pancreatic cells that produce insulin
- PET Scan: Positron Emission Tomography imaging technique
- GLP1 Receptor: Molecular target on insulinoma tumors
- Exendin: Modified version of Gila monster saliva compound
- Insulin: Hormone regulating blood sugar levels
Quiz
- What percentage of insulinomas does the new scan detect?
- What animal’s saliva provided the basis for the new scanning technology?
- What was the previous surgical approach when tumors couldn’t be located?
Answers:
- 95%
- Gila monster
- Surgeons would progressively cut away portions of the pancreas until finding the tumor
Enjoy this story? Get our newsletter! https://scienceblog.substack.com/
Further Reading: Journal of Nuclear Medicine Article
If our reporting has informed or inspired you, please consider making a donation. Every contribution, no matter the size, empowers us to continue delivering accurate, engaging, and trustworthy science and medical news. Independent journalism requires time, effort, and resources—your support ensures we can keep uncovering the stories that matter most to you.
Join us in making knowledge accessible and impactful. Thank you for standing with us!