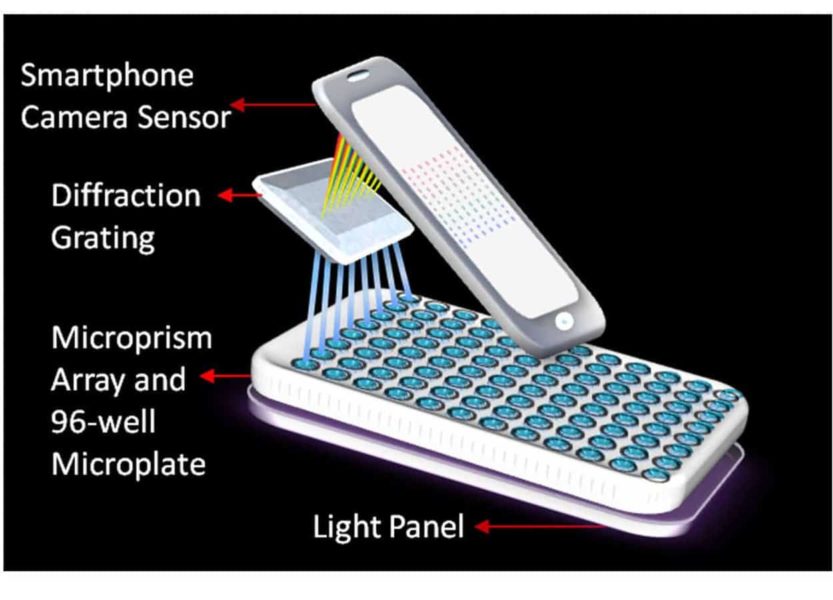
Washington State University researchers have developed a low-cost, portable laboratory on a smartphone that can analyze several samples at once to catch a cancer biomarker, producing lab quality results.
The research team, led by Lei Li, assistant professor in the School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, recently published the work in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956566316308983).
At a time when patients and medical professionals expect always faster results, researchers are trying to translate biodetection technologies used in laboratories to the field and clinic, so patients can get nearly instant diagnoses in a physician’s office, an ambulance or the emergency room.
The WSU research team created an eight channel smartphone spectrometer that can detect human interleukin-6 (IL-6), a known biomarker for lung, prostate, liver, breast and epithelial cancers. A spectrometer analyzes the amount and type of chemicals in a sample by measuring the light spectrum.
Although smartphone spectrometers exist, they only monitor or measure a single sample at a time, making them inefficient for real world applications. Li’s multichannel spectrometer can measure up to eight different samples at once using a common test called ELISA, or colorimetric test enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, that identifies antibodies and color change as disease markers.
Although Li’s group has only used the smartphone spectrometer with standard lab-controlled samples, their device has been up to 99 percent accurate. The researchers are now applying their portable spectrometer in real world situations.
“With our eight channel spectrometer, we can put eight different samples to do the same test, or one sample in eight different wells to do eight different tests. This increases our device’s efficiency,” said Li, who has filed a provisional patent for the work.
“The spectrometer would be especially useful in clinics and hospitals that have a large number of samples without on-site labs, or for doctors who practice abroad or in remote areas,” he said. “They can’t carry a whole lab with them. They need a portable and efficient device.”
Li’s design works with an iPhone 5. He is creating an adjustable design that will be compatible with any smartphone.
The work was funded by the National Science Foundation and a WSU startup fund. It is in keeping with WSU’s Grand Challenges, a suite of research initiatives aimed at large societal issues. It is particularly relevant to the challenge of sustaining health and its themes of healthy communities.
If our reporting has informed or inspired you, please consider making a donation. Every contribution, no matter the size, empowers us to continue delivering accurate, engaging, and trustworthy science and medical news. Independent journalism requires time, effort, and resources—your support ensures we can keep uncovering the stories that matter most to you.
Join us in making knowledge accessible and impactful. Thank you for standing with us!