Summary: Scientists have developed a novel antibody that combines three cancer-fighting functions in one: targeting cancer cells, delivering treatment, and activating the immune system. The treatment, which proved effective in mouse studies, could offer a faster path from diagnosis to personalized cancer treatment.
Journal: Nature Communications, November 11, 2024, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53839-5 | Reading time: 4 minutes
A Three-Pronged Attack on Cancer
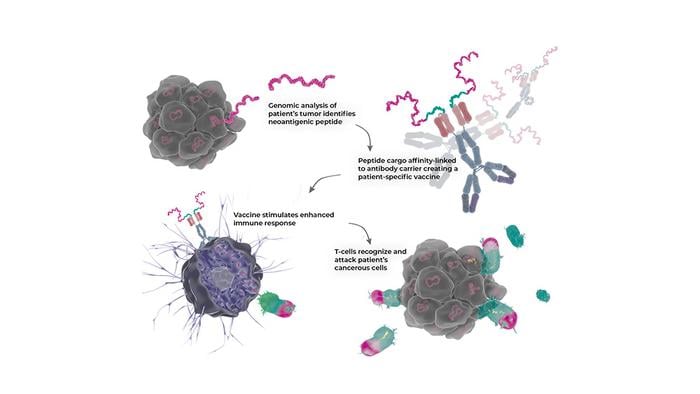
Cancer treatment often requires multiple approaches working together. Now, researchers at Uppsala University and KTH Royal Institute of Technology have developed an antibody that combines three critical functions in one treatment.
“We have been researching precision medicine for close to 15 years now, as well as how we can use antibodies to influence an important key protein (CD40) in the immune system. We can now show that our new antibody method works as precision medicine for cancer,” explains Sara Mangsbo, professor at Uppsala University’s Department of Pharmacy.
Training the Immune System
The new treatment works by redirecting the immune system to find and target specific mutations that occur only in cancer cells, known as neoantigens. The antibody delivers tumor-specific material directly to immune cells while simultaneously stimulating them, enhancing the body’s natural defense against cancer.
In testing, the method showed promising results. It successfully activated the right type of immune cells in human blood samples. In animal studies, mice receiving the treatment showed extended survival, with higher doses protecting them from cancer entirely.
Faster Path to Treatment
While customized precision medicines can be expensive and slow to develop, this new approach offers potential advantages. “The advantage of our drug is that it is easy to produce on a larger scale, yet can be easily tailored to the patient’s disease or specific tumour,” notes Johan Rockberg, Professor at KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
The treatment consists of two parts: a targeting bispecific antibody that can be mass-produced in advance, and a custom peptide component that can be quickly synthesized for specific cancer types. This design could reduce both production costs and the time between diagnosis and treatment.
Glossary
- Antibody: A protein produced by the immune system to fight disease
- Neoantigens: Mutations found only in cancer cells
- Bispecific antibody: An antibody designed to recognize two different targets
- Peptide: A small protein molecule
Quiz
- What three functions does the new antibody combine?
Answer: Targeting cancer cells, delivering treatment, and activating the immune system - How long have the researchers been studying precision medicine?
Answer: Close to 15 years - What did the treatment achieve in mouse studies?
Answer: Extended survival and protected from cancer at higher doses - What are the two main components of the treatment?
Answer: A targeting bispecific antibody and a custom peptide component
Enjoy this story? Get our newsletter! https://scienceblog.substack.com/
If our reporting has informed or inspired you, please consider making a donation. Every contribution, no matter the size, empowers us to continue delivering accurate, engaging, and trustworthy science and medical news. Independent journalism requires time, effort, and resources—your support ensures we can keep uncovering the stories that matter most to you.
Join us in making knowledge accessible and impactful. Thank you for standing with us!