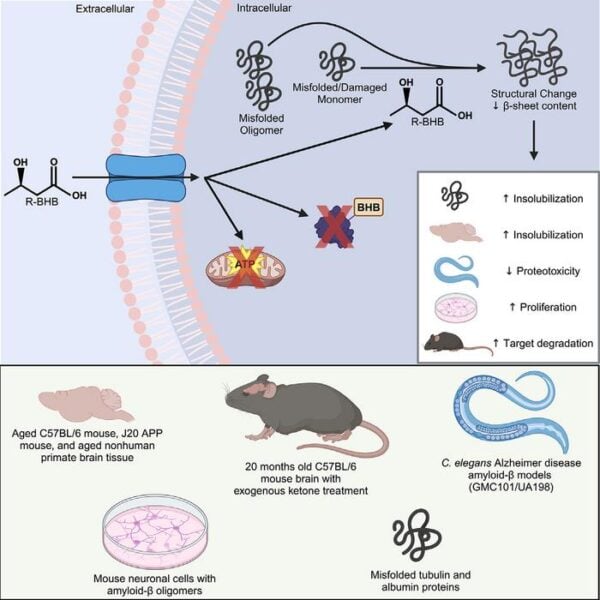
When our bodies are low on glucose from food, they produce ketone bodies as an alternative fuel source. While scientists have long known that ketones can power brain cells, new research from the Buck Institute for Research on Aging has uncovered a surprising additional role: ketone bodies act as molecular janitors, helping to clear away misfolded proteins that can accumulate and cause damage in aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
“Now we know that’s not the whole story,” explains senior author John Newman, MD, PhD. “Ketone bodies interact with damaged and misfolded proteins directly, making them insoluble so they can be pulled from the cell and recycled.” This discovery provides crucial insight into why ketogenic diets and fasting may benefit brain health.
The research team, led by PhD candidate Sidharth Madhavan, found that the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) can bind directly to problematic proteins, changing their structure in a way that marks them for removal by the cell’s waste disposal systems. They demonstrated this effect both in isolated proteins and in living organisms, showing that ketone treatment could prevent the toxic effects of protein accumulation.
In a striking demonstration, the researchers found that adding ketones helped restore movement in nematode worms engineered to produce human amyloid-beta, a protein that forms plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. The treated worms maintained their ability to swim, while untreated worms became paralyzed as toxic proteins accumulated.
The findings suggest that ketone bodies serve a dual purpose during periods of fasting or ketogenic dieting: they not only provide fuel for brain cells but also trigger cleanup of damaged proteins that could otherwise lead to disease. “It’s beautiful to imagine that changing metabolism results in this symphony of molecules cooperating together to improve brain function,” Newman notes.
Glossary
- Ketone bodies
- Small molecules produced by the liver when glucose is scarce, serving as an alternative energy source
- Proteostasis
- The balanced regulation of protein production, folding, and degradation in cells
- Amyloid-beta
- A protein that can accumulate into toxic clumps in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients
- β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)
- The main ketone body produced during fasting or ketogenic diets
Test Your Knowledge
What is the newly discovered function of ketone bodies in the brain?
Beyond providing energy, ketone bodies can bind to misfolded proteins and help mark them for removal from brain cells.
How did researchers demonstrate the protective effects of ketones in living organisms?
They showed that ketone treatment prevented paralysis in nematode worms engineered to produce human amyloid-beta protein.
What is the mechanism by which β-hydroxybutyrate affects problematic proteins?
BHB binds directly to misfolded proteins, making them insoluble and targeting them for clearance through cellular recycling systems.
Why might these findings explain the benefits of fasting and ketogenic diets for brain health?
The research suggests ketones produced during these metabolic states not only fuel brain cells but also actively help clear away damaging protein accumulations that could lead to cognitive decline and disease.
If our reporting has informed or inspired you, please consider making a donation. Every contribution, no matter the size, empowers us to continue delivering accurate, engaging, and trustworthy science and medical news. Independent journalism requires time, effort, and resources—your support ensures we can keep uncovering the stories that matter most to you.
Join us in making knowledge accessible and impactful. Thank you for standing with us!